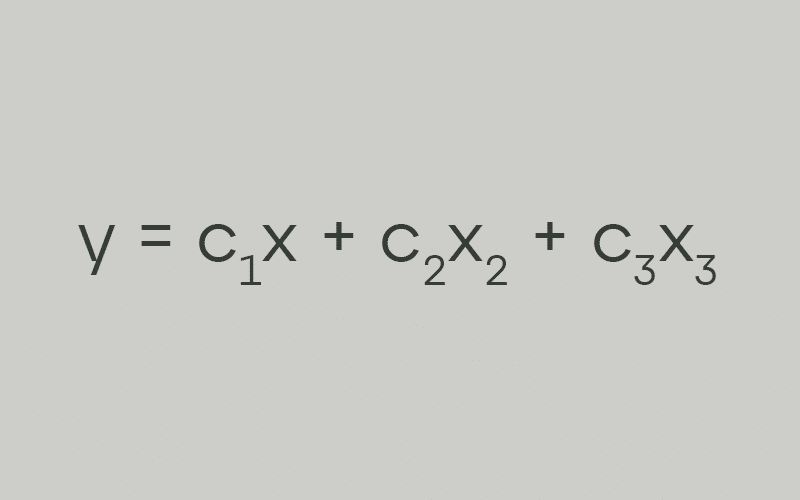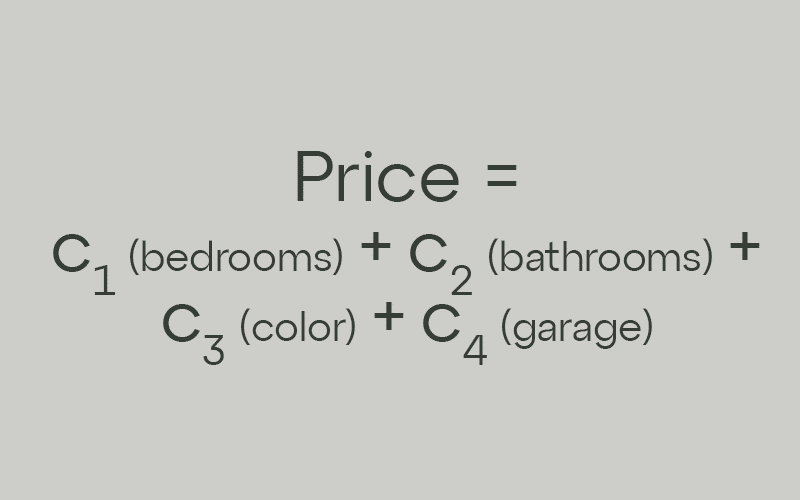Types of Linear Regression
Ordinary Least Squares
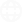
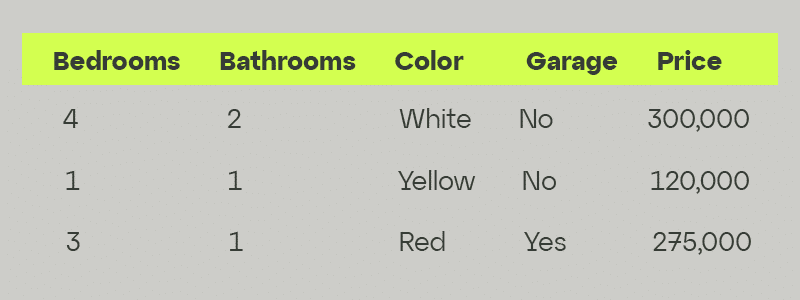
Ordinary Least Squares attempts to minimize the sum of the square residuals. Imagine our dataset as a 2d Matrix of points where each point in the matrix is an example in our dataset. OLS attempts to draw a line through the matrix that has the shortest distance from the line to every point in the matrix.
Gradient Descent
With Gradient descent the coefficients are initially determined randomly, they are then adjusted depending on the learning rate (α), which is set by the user. The coefficient is adjusted in the direction of reducing the error.
Regularization
Regularization attempts to reduce the complexity of the model while also reducing the error at the same time. 2 examples of Regularization are:
Lasso Regression
Lasso Regression is a modified OLS that also minimizes the absolute sum of the coefficients.
Ridge Regression
Ridge Regression is also a modified OLS that minimizes the squared absolute sum of the coefficients.
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned: