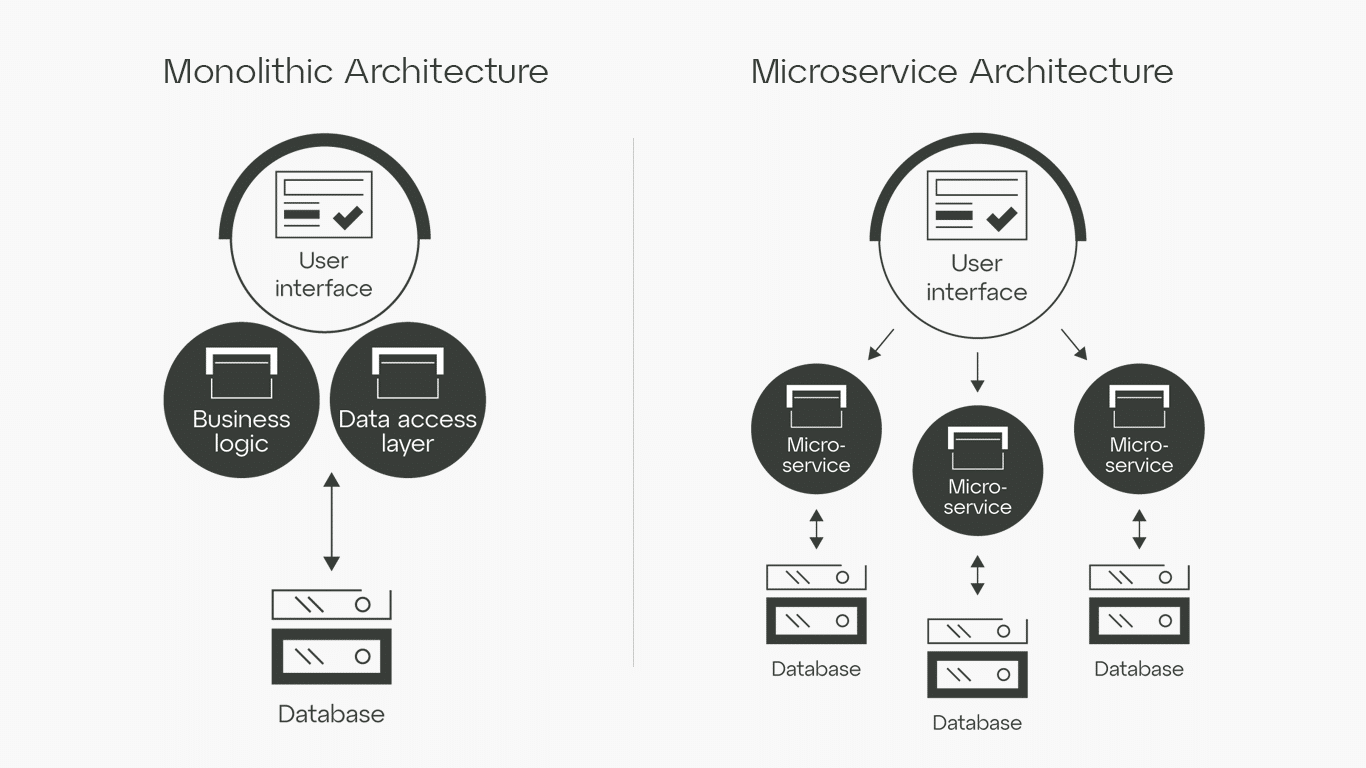
As organizations strive to deliver high-quality software and services at scale, many are turning to a microservices architecture as a way to break down monolithic applications into smaller, more manageable components. By decoupling application functionality and deploying it as independent microservices, organizations can achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and resiliency in their applications.
In this blog, I will showcase the steps involved in migrating a monolithic application to the cloud using microservices. Concurrently, we will cover the entire lifecycle of the migration process, from evaluating the existing monolithic application to planning and building the microservices architecture to deploying and managing the microservices in the cloud. By following these steps, organizations can successfully move to microservices and reap the benefits of a more agile and scalable architecture.